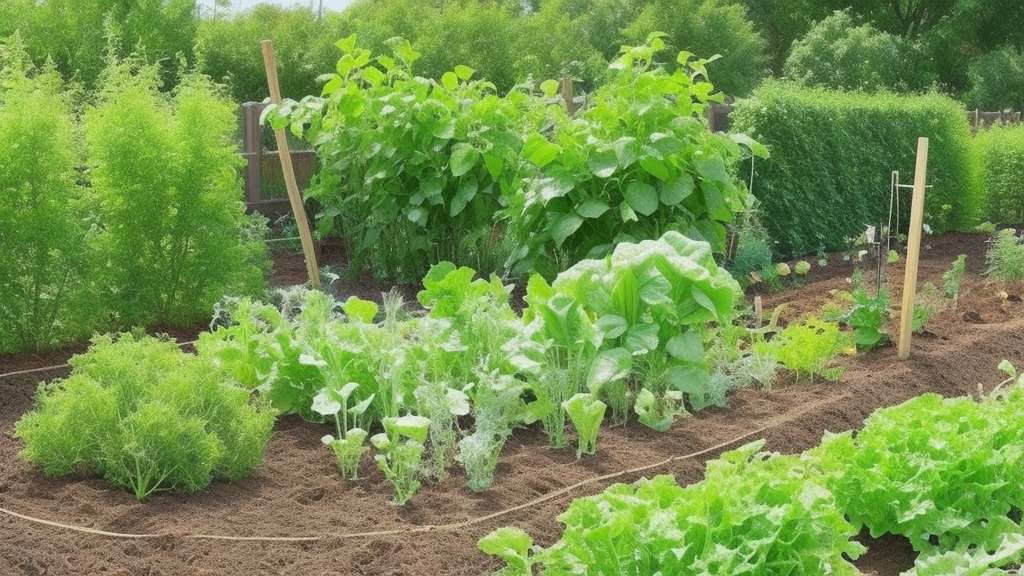
What Vegetables Should Not Be Planted Next to Each Other? Avoid These Incompatible Vegetables in Your Garden
Incompatible Vegetables Key Ideas
- Understanding plant incompatibility and good companion plants is crucial for successful gardening, as certain vegetables can negatively impact each other’s growth and health.
- Common incompatible vegetable pairs, such as tomatoes, potatoes, cucumbers, and sage, are important plant incompatibilities to consider when planning your garden layout.
- Some vegetables clash due to their chemical composition or susceptibility to similar pests and diseases, highlighting the need for strategic placement in the garden and companion plantings.
- To avoid growth issues and disease, consider companion planting with compatible vegetables to promote mutual benefits and natural pest control, and avoid incompatible garden plants.
- Maximizing garden space with compatibility involves companion plantings, such as planting carrots near peas, to enhance soil quality and nutrient uptake.
- Tips for successful companion planting include rotating crops annually, interplanting flowers with vegetables for pest management, and utilizing trellises for vertical gardening.
- Extensive Seed Starter Kit: This heirloom seeds pack offers 32 different heirloom vegetable varieties, providing a comprehensive assortment to diversify your garden and ensure a bountiful harvest
- High-Yield Potential: With 15,000 plant seeds included, this pack is designed to produce a substantial amount of fresh, homegrown vegetables, supporting both small and large-scale gardening projects
- Non-GMO and Heirloom Quality: All garden seeds are non-GMO and heirloom, ensuring natural growth and the ability to save seeds for future planting, promoting sustainability in your gardening practices
- Ideal for Emergency Preparedness: This seed vault serves as a valuable addition to survival gear and emergency supplies, providing a reliable food source during unforeseen circumstances
- Sustainable Living Support: Growing seeds for planting vegetables promotes a sustainable lifestyle, lessening environmental impact while offering a rewarding, hands-on approach to healthy eating
Last update on 2025-11-13 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
Did you know that certain vegetables can harm each other’s growth when planted side by side, especially with incompatible garden plants and companion plantings?
Understanding which vegetables and incompatible garden plants should not be planted next to each other is crucial for companion plantings and a successful and bountiful harvest.
Avoiding incompatible pairings and considering companion plantings can prevent stunted growth, disease susceptibility, and yield reduction in your garden.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting, this information, including companion plantings, will help you optimize your garden layout, promote healthier plants, and maximize your harvest.
Stay tuned to learn about the surprising companion plantings hindering your vegetable garden’s productivity.
Incompatible Vegetables Cheat Sheet
Vegetable Companion Planting Guide
Companion planting is an effective gardening technique that improves plant health and growth. However, some vegetables should not be planted next to each other as they can inhibit each other’s growth or attract pests. Here is a detailed guide on which vegetables should not be planted together.
Incompatible Vegetable Pairings
| Vegetable | Should Not Be Planted With | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Cabbage, Corn, Potatoes | Compete for nutrients, attract similar pests. |
| Carrots | Dill, Parsnip | Dill stunts carrot growth, parsnip competes for nutrients. |
| Beans | Onions, Garlic | Onions and garlic inhibit bean growth. |
| Cucumbers | Potatoes | Potatoes increase risk of blight. |
| Onions | Beans, Peas | Onions inhibit growth of beans and peas. |
| Peas | Onions, Garlic | Onions and garlic inhibit pea growth. |
| Potatoes | Tomatoes, Cucumbers | Increase risk of blight and compete for nutrients. |
| Radishes | Hyssop | Hyssop inhibits radish growth. |
| Spinach | Potatoes | Compete for nutrients. |
Additional Resources
Understanding Plant Incompatibility
Allelopathic Properties
Vegetables possess allelopathic properties and can be used in companion plantings, which means they release biochemicals that can inhibit the growth of neighboring plants.
For instance, garlic and onions inhibit the growth of many garden vegetables, such as beans and peas, due to their allelopathic nature, making them unsuitable for companion plantings.
This can lead to stunted growth or reduced yield for the affected vegetables and companion plantings.
Incompatible Garden Plants
Due to their incompatible nature, certain vegetable combinations, especially in companion plantings, can result in poor growth or even harm each other.
For example, planting cucumbers near potatoes can decrease potato yields, as cucumbers release substances that can negatively affect potato plants.
Similarly, growing tomatoes near cabbage can adversely impact the growth of both plants.
Understanding these incompatibilities is crucial for successful gardening as it directly influences the health and productivity of the garden.
Planning for Vegetable Placements
When planning a vegetable garden, it’s essential to consider the compatibility of different plants.
Gardeners can optimize plant growth and maximize yields by strategically placing vegetables based on compatibility.
For instance, pairing carrots with peas can be beneficial. Carrots can provide a sturdy base for the plant, helping to support pea vines without inhibiting their growth.
Moreover, considering the rotation of crops and plants is also important to prevent the buildup of diseases and pests that may affect specific vegetables.
Rotating crops helps maintain soil fertility and prevents the depletion of nutrients by specific plants.
Common Incompatible Vegetable Pairs
Cabbage and Tomatoes
Cabbage and tomatoes should not be planted next to each other. Cabbage secretes a substance that inhibits tomato growth, leading to stunted plants and reduced yields.
When cabbage and tomatoes are grown together, they compete for nutrients in the soil, resulting in poor growth and development for both plants.
Potatoes and Tomatoes
Potatoes and tomatoes are incompatible due to their susceptibility to similar diseases, such as blight.
Planting them together increases the risk of disease spread, affecting the overall yield.
Tomatoes also release solanine, which is toxic to potatoes. This can lead to decreased potato production and quality.
Beans and Onions
Planting beans and onions together is not advisable.
Beans inhibit the growth of onions, leading to reduced yields due to competition for resources between the two plant species.
Furthermore, onions emit compounds that can hinder the germination and growth of beans, impacting their overall productivity, plant.
Carrots and Dill
Carrots and dill are incompatible because dill releases chemicals that can stunt carrot growth. This interference affects the size and flavor of the carrots.
Planting these two together can attract pests targeting carrots, potentially damaging the crop.
Zucchini and Potatoes
Growing zucchini and potatoes nearby is discouraged due to their differing water requirements when planting.
Zucchinis thrive in well-drained soil with consistent moisture, while potatoes require a more moderate moisture level for planting.
Planting them together may lead to uneven watering practices, affecting the growth of both crops.
Peas and Summer Squash
Avoid planting peas and summer squash together as they have different spacing requirements.
Summer squash tends to spread out extensively, overshadowing and crowding out pea plants.
This can result in decreased pea yields and hinder their overall growth due to plant disease.

Why Some Vegetables Clash
Chemical Reactions
Due to chemical reactions, certain vegetables should not be planted next to each other.
For instance, planting cabbage near strawberries can lead to a clash.
This is because cabbage, being a plant, secretes allelochemicals that are detrimental to the growth of strawberries.
One plant’s release of these chemicals can inhibit the growth of another. Similarly, onions and beans should be kept apart.
Onions release compounds that can impede the growth of beans, affecting their development and yield.
Nutrient Competition
In the vegetable world, some plants compete for specific nutrients in the soil. For example, tomatoes and potatoes belong to the same family and require significant nutrients from the soil.
They compete for these essential nutrients when planted together, leading to stunted growth and diminished crop yields.
Moreover, carrots and dill are incompatible due to their distinct plant nutrient requirements. Carrots need phosphorus, while dill requires a high level of nitrogen.
Planting them together can result in inadequate nutrient availability for either crop, impacting their overall health and productivity.
Soil-Borne Diseases
Certain vegetables also carry diseases that can affect neighboring plants.
For instance, planting cucumbers near melons can lead to cross-contamination of soil-borne diseases such as Fusarium wilt.
This disease affects cucumber and melon plants, causing wilting and reduced fruit production.
Planting peppers near fennel can result in disease susceptibility.
Peppers are vulnerable to various diseases, and when planted close to fennel, they become more susceptible to fungal infections such as fusarium wilt or blight.
- Sturdy and Stainless Steel Garden Set: Made of Stainless Steel, this stainless steel gardening tools is durable and rust-proof. Moreover, with stable material like this, these gardening tools are hardly deformed
- One for All Package: Grenebo garden tools set includes a total of 8 tools and 1 storage bag. Pruning Shears, Weedier, Transplanter, Cultivator, etc., nearly everything you need in daily garden maintenance
- Ergonomic Handle Design: In order to realize a more comfortable and effortless user experience, the gardening tools were non-slipped wooden handles, well-designed and suitable for different hand sizes. No matter kids or seniors, these gardening tools made things easy during digging, carrying, weeding, planting, and pruning
- Garden Tote Bag: The biggest concern of buying a big gardening tool set is storage, but for this consideration, Grenebo gardening tools for gardening come with a heavy-duty storage bag, is floral design with a vintage style, adds additional beauty to your garden. Moreover, there is a specialized hole on each tool handle for hanging them up in the off-season or after use
- Show your love with a premium Garden Tools Set: The tote bag durable and easy to carry, which is the choice for women, neighbors, and all enthusiastic gardening lovers
Last update on 2025-11-13 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
Avoiding Growth Issues and Disease
Proximity Impact
When planting vegetables, it’s crucial to understand the impact of proximity on their growth.
Certain vegetables, when planted, release chemicals that can inhibit the growth of others.
For instance, members of the nightshade family, such as tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants, should not be planted near each other due to their susceptibility to similar diseases.
Plants with different nutrient needs should be kept apart. Heavy feeders, like corn and squash, can deplete the soil of vital nutrients, affecting the growth of neighboring plants.
Pest Control Measures
Plant your garden strategically to prevent the spread of pests among vegetables.
For example, planting carrots near tomatoes can attract carrot flies that may damage the plants.
Understanding these interactions can help prevent infestations and maintain plant health.
Moreover, certain vegetables create shade as they grow taller, affecting nearby plants’ access to sunlight.
It’s important to consider this when planning your garden to ensure that all plants receive adequate sunlight for healthy growth.
Companion Planting Benefits
Strategic companion planting can help prevent disease and promote healthy growth. For instance, planting marigolds alongside vegetables can deter pests due to their strong scent.
Similarly, growing basil near tomatoes can improve their flavor while repelling pests affecting tomatoes.
Furthermore, rotating crops annually can help break pest and disease cycles by disrupting their habitat and reducing the risk of recurrence.
Maximizing Garden Space with Compatibility
Strategic Planting
When planning your vegetable garden, consider companion planting to optimize your space.
This involves strategically placing vegetables together based on their compatibility and mutual benefits.
For instance, planting tomatoes alongside carrots can help deter pests and maximize space utilization.
Enhancing Growth and Yield
Understanding which vegetables complement each other and how to plant them can enhance the growth and yield of your crops.
For example, pairing lettuce with tall plants like corn or beans can provide shade and shelter, promoting healthier growth.
Intercropping vegetables such as radishes with spinach can help deter pests, optimize space, and plant.
Creating a Harmonious Layout
Utilize the concept of compatibility to plant and create a harmonious and productive garden layout.
For instance, planting vegetables that compete for similar nutrients separately can prevent stunted growth and yield reduction.
To prevent nutrient depletion in the soil, avoid planting competitive crops such as cucumbers and potatoes next to each other.
Tips for Successful Companion Planting
Spacing Techniques
Proper spacing techniques are crucial when companion planting to ensure each plant receives adequate nutrients.
Avoid overcrowding to prevent competition for resources such as water and sunlight. Adequate spacing also helps reduce the risk of diseases spreading among closely situated plants.
Consider Growth Habits
Consider the growth habits, nutrient requirements, and plant vegetables when planning your garden. Some plants have deep roots, while others have shallow ones.
Pairing deep-rooted plants with shallow-rooted ones can help maximize space and nutrient uptake.
For instance, planting carrots alongside tomatoes allows the carrots to utilize the soil beneath the plants’ shallow roots.
Nutrient Interactions
Understanding the nutrient interactions between different vegetables is essential for successful companion planting.
Certain vegetables may release chemicals into the soil that benefit neighboring plants, while others may inhibit the growth of nearby vegetables.
For example, legumes like beans and peas fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits nitrogen-loving plant crops like corn and leafy greens.
Crop Rotation
Implementing a crop rotation schedule is crucial for maintaining soil health and preventing the buildup of pests and diseases.
Rotate and plant your vegetable crops annually to minimize soil depletion and reduce the risk of pest infestations.
This technique also helps break disease cycles by preventing pathogens from building up in the soil.
Pest Control
Certain plants act as natural pest repellents for others.
For instance, planting marigolds alongside tomatoes can help deter pests that commonly affect tomato plants.
Incorporating aromatic herbs like basil and rosemary into your vegetable garden can repel insects while enhancing the flavor of neighboring vegetables.
Succession Planting
Utilize succession planting to maximize your garden space throughout the growing season.
After harvesting early-season crops like lettuce or radishes, replant the same area with a different vegetable to ensure continuous production.
This technique maximizes yield, optimizes space utilization, and plants in your garden.
- Each raised metal garden bed size: 4×2×1ft ,7.14Cu
- Upgraded quality and structure: raised garden beds outdoor are made of Q195 galvanized metal sheet, double-layer anti-corrosion galvanizing and oval structure design, which is more beautiful, can withstand greater pressure at the interface, is not easy to loose, and the interface will not Deformed and can be reused for many years.
- Easy to set up, this galvanized stock tank only takes about 5 minutes to easily assemble and continue planting plants.
- Open base: This planter raised garden bed metal galvanized is designed with an open base, which can effectively avoid water accumulation and decay, protect the roots of plants, and allow the roots to better absorb nutrients
- Double thickness: The average thickness of this galvanized planter galvanized sheet reaches 0.78mm, and the thickest part can reach 1.56mm, which is extremely stable. Compared with the ordinary rectangular elevated garden bed with a thickness of 0.3mm, it will be the right choice for you. buy it! ! !
Last update on 2025-11-13 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
Alternative Planting Suggestions
Companion Planting
Regarding companion planting, certain vegetables should not be planted next to each other due to their incompatible nature.
For instance, planting broccoli near tomato plants is not advisable as it can attract pests and stunt the growth of both crops.
Creative Separation
Consider using creative separation techniques such as intercropping or vertical gardening to overcome this issue.
Intercropping involves planting different crops to maximize space and reduce competition for resources.
This technique allows you to plant and separate incompatible vegetables effectively while maximizing the use of your garden space.
Crop Rotation
Another alternative is crop rotation, which involves changing the location of specific plant families each season.
By rotating your crops and plants, you can prevent the buildup of pests and diseases associated with certain vegetables.
For example, if you previously planted tomatoes in a particular area, consider planting several root crops or delicate pea plants in that spot the following season.
Raised Beds
Raising beds is also an effective method to separate incompatible vegetables and plants.
Creating distinct planting areas for each crop can prevent them from interfering while optimizing growing conditions.
For instance, you can plant fennel or eggplant in one raised bed and potatoes in another to avoid detrimental effects on their growth.
Using Barriers
When planting, consider incorporating physical barriers such as trellises or fencing to separate incompatible vegetables.
This strategy is particularly useful for sunflower seedlings, which can overshadow neighboring crops if not separated adequately.
Using barriers also supports climbing plants like peas and beans, ensuring they do not intertwine with incompatible neighbors.
Container Gardening
For those with limited space, container gardening offers a versatile solution for separating incompatible vegetables and plants.
By planting different crops in individual containers, you can easily control their growing environment and prevent them from negatively influencing each other.
This method especially benefits new onion transplants, allowing you to keep them isolated from other incompatible crops.
Incompatible Vegetables Closing Thoughts
Now that you understand the potential clashes between certain vegetables, you can make informed decisions to optimize your garden by choosing the right plants.
Avoiding incompatible pairings and embracing companion planting can maximize space, reduce disease risk, and promote healthier vegetable growth.
Remember to refer to the common incompatible vegetable pairs and alternative planting suggestions when planning your garden layout.
As you embark on your gardening journey, experiment with these tips and observe how your plants interact.
Share your experiences with other gardening enthusiasts and continue learning about companion planting to enhance your gardening skills further.
Happy planting!
Incompatible Vegetables Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common incompatible vegetable pairs?
Common incompatible vegetable pairs include tomatoes, potatoes, cucumbers, and sage. These combinations can lead to growth issues and disease due to competing for nutrients or attracting pests that harm one another.
Why is it important to understand plant incompatibility?
Understanding plant incompatibility is crucial for successful gardening as it helps avoid growth issues, diseases, and poor yields. By planting compatible vegetables together, you can maximize garden space, promote healthier growth, and reduce the need for chemical interventions.
How can I maximize my garden space with compatibility?
Maximizing your garden space with compatibility involves strategically planting vegetables that complement each other’s growth patterns and nutrient needs. This allows you to maximize limited space while promoting healthy plant growth and enhancing overall garden productivity.
What are some alternative planting suggestions for incompatible vegetables?
If you have incompatible vegetables, consider planting them in separate areas or using physical barriers to prevent their roots from interacting. Alternatively, focus on companion planting by selecting vegetables that support each other’s growth and health, creating a harmonious garden environment.
What are some tips for successful companion planting?
Successful companion planting involves considering factors such as sunlight requirements, soil preferences, and pest-repelling properties of different vegetables. By understanding these dynamics and carefully planning your garden layout, you can create a thriving ecosystem where plants benefit each other’s growth and yield.